The main causes of erectile dysfunction at 40 include low testosterone levels, cardiovascular problems, emotional factors such as stress and anxiety, smoking, and obesity. However, with simple habits and regular consultations, it is possible to prevent the problem. Learn more.
At 40, many men face challenges related to sexual health, such as erectile dysfunction. Common at this stage of life, this condition may have various causes, from physical factors like hormonal changes and cardiovascular issues to emotional problems like stress and anxiety.
But don’t worry: identifying the causes is the first step to regaining quality of life and confidence in sexual performance. Discover the key factors contributing to the condition and the available treatment options.
Erectile Dysfunction at 40: Main Causes
The primary cause of erectile dysfunction is age. From the age of 30-35, testosterone levels start to decline, dropping by 1% to 2% per year by 40.
As testosterone decreases, the body produces less nitric oxide, a substance crucial for dilating penile blood vessels (which increases blood flow necessary for an erection).
Other causes of erectile dysfunction include conditions affecting circulation, such as diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, obesity, and smoking.
Medication use, stress, anxiety, and depression are also linked to sexual impotence.

Cardiovascular Problems
Cardiovascular problems are risk factors for erectile dysfunction. Issues like hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis, obesity, and smoking damage arteries, preventing blood from circulating to the penis during arousal.
According to this article, erectile dysfunction is more common in men with coronary artery disease (CAD) than in those without. CAD is a cardiovascular disease caused by atherosclerosis affecting the arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle.
Aging
According to this study, “Diagnosis and Treatment of Testosterone Deficiency: A Review,” testosterone reduction begins between the ages of 35-40.
The study also highlights that a survey of 2,162 men over 45 revealed that 35% to 40% of participants had testosterone levels below 300 ng/mL.
The hormone’s decline makes it harder to achieve penile rigidity after 40 due to reduced capacity of the corpora cavernosa tissues to expand. As a result, these tissues fail to fill with blood, leading to insufficient erection for penetration.

Hormonal Decline
In addition to natural testosterone reduction, erectile dysfunction at 40 can result from gonadal problems, as the gonads produce hormones regulating sexual characteristics and libido.
Issues with the pituitary gland, which regulates the release of hormones, also contribute to hormonal decline. Pituitary problems causing hormonal drops include:
- Hyperprolactinemia: increased prolactin levels, a hormone stimulating milk production. In men, it reduces libido, hampers erection, decreases body hair, and increases breast tissue.
- Cushing’s Disease: genetic or caused by prolonged corticosteroid use or pituitary tumors, this condition leads to excess cortisol, potentially resulting in erectile dysfunction.
- Hypopituitarism: inadequate hormone production by the pituitary, possibly congenital or caused by infections like meningitis and tuberculosis, or cranial radiotherapy.
Testicular diseases like orchitis, varicocele, and cancer also lower testosterone levels by impairing Leydig cells in the testes responsible for testosterone production.
Diabetes
Excess sugar damages circulation in extremities like the penis, obstructing arteries. Without blood flow to the corpora cavernosa, they can’t fill with blood, preventing a firm erection.
Diabetes also promotes fibrosis formation, small lesions from attempting penetration without a fully rigid penis. Left untreated, these fibroses can cause penile curvature, known as Peyronie’s disease.
Hypertension
Hypertension forces the heart to work harder to distribute blood. When untreated, it impairs overall circulation, including to the penis, preventing it from becoming fully engorged and rigid.
Obesity
The obesity-erectile dysfunction link operates on two fronts. First, the pituitary gland becomes dysregulated, reducing testosterone production. Second, obesity predisposes individuals to conditions harming cardiovascular health, like diabetes and hypertension.
Smoking
Smoking causes erectile dysfunction by hardening and narrowing blood vessels, restricting blood flow to the penis and preventing satisfactory erections.
Smoking also reduces nitric oxide production, a substance dilating blood vessels and increasing blood flow to the penis.
While it’s unclear how long smoking takes to cause impotence, prolonged exposure increases cardiovascular health risks.
Electronic cigarettes also lead to erection issues due to nicotine-induced endothelial inflammation, narrowing and hardening arteries.
Stress, Anxiety, or Depression
Stress harms sexual health by triggering excessive cortisol release. The “stress hormone” interferes with testosterone production, which regulates libido and nitric oxide production, critical for penile blood flow.
Regarding anxiety, this article, “Erectile Dysfunction in Patients with Anxiety Disorders: A Systematic Review,” reviewed 12 studies on erectile dysfunction in men with anxiety disorders. The authors found high rates of erectile dysfunction in participants with anxiety diagnoses.
For depression, this study highlights erectile difficulties in 35% to 47% of depressed men.
Medications
Some medications can cause erectile dysfunction. This article that analyzed the Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) identified 20 medications associated with erectile dysfunction between 2010 and 2020.
Of the 6,142 ED reports, 2,442 were caused by neuropsychiatric drugs. Finasteride and dutasteride, used for hair loss, also contain substances that list erectile dysfunction as a side effect.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for erection problems at 40 are related to lifestyle.
Poor diet, obesity, smoking, hypertension, diabetes, medication use, and emotional issues negatively impact male sexual health by impairing blood circulation and testosterone production.
Does Erectile Dysfunction at 40 Have a Cure?
Yes. Erectile dysfunction at 40 can be treated. Medical monitoring is essential to identify the causes and determine the most appropriate treatment. When the problem is recurrent, men should consult a urologist, as they specialize in the male sexual system and are equipped to identify the origin and best treatment for impotence.
Pharmacological Treatments
Treatment for male impotence at 40 includes oral medications, penile injections, and hormonal therapies. Check out the options:
- Oral Medications: The first treatment option includes drugs like Sildenafil, Tadalafil, Vardenafil, and Avanafil. All require erotic stimulation to work, with the main difference being their duration of action. For instance, Sildenafil works for 5 hours;
- Penile Injections: These do not require erotic stimulation and are usually prescribed when oral medications fail;
- Hormonal Therapies: Hormone replacement therapy is recommended when testosterone levels are below 300 ng/mL.
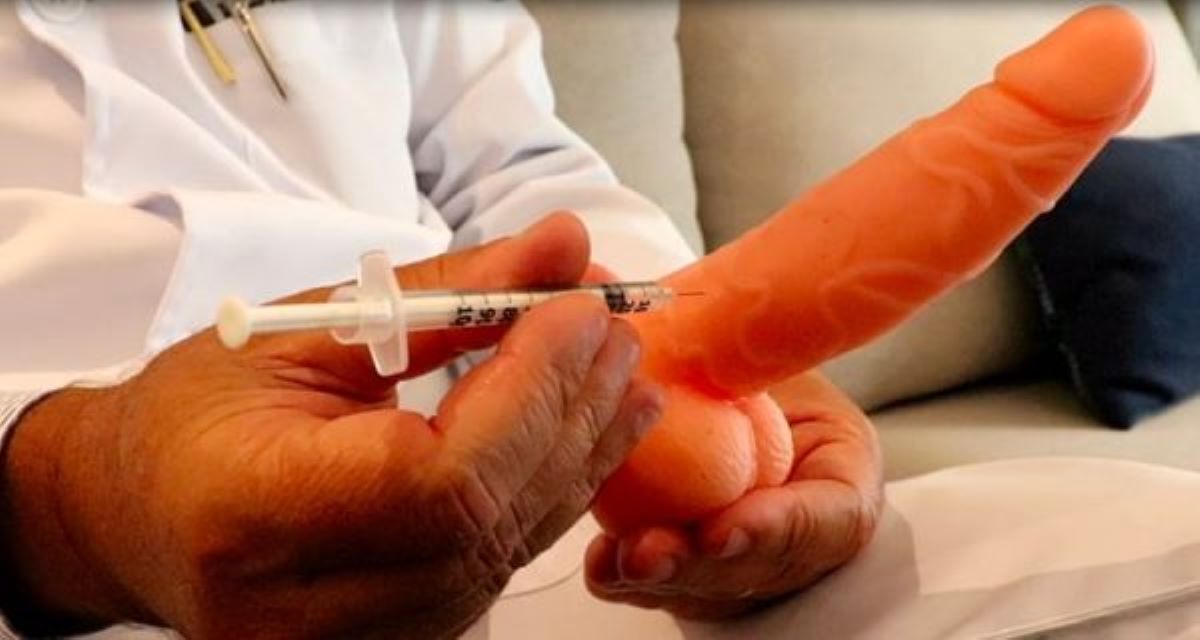
Non-Pharmacological Therapies
The vacuum penile pump creates a vacuum around the member, increasing blood flow to the region.
Penile prostheses are indicated for severe erectile dysfunction not resolved with medications, penile injections, or vacuum devices. Other indications include Peyronie’s disease and cases where nerves responsible for erection are compromised after prostate cancer surgery.
Healthy Habits to Incorporate into Your Routine
Adopting healthy habits can contribute to sexual health and overall well-being. Here are the main ones:
- Take Care of Cardiovascular Health: Maintain a healthy diet, engage in physical activity, avoid excessive alcohol, and do not smoke;
- Take Care of Mental Health: Stress and anxiety increase cortisol levels, the “stress hormone,” which impairs testosterone production. To address this, try meditation, yoga, or psychotherapy;
- Regular Check-Ups: Annual check-ups help identify hormonal reductions that affect male sexual health.
Erectile dysfunction at 40 can be challenging, but with healthy habits and specialized medical care, significant improvement is possible. Adopting healthy habits, taking care of mental health, and seeking specialized medical follow-up are key steps to overcoming this challenge. By prioritizing your health and seeking professional help, you are on the right track to a satisfying and fulfilling sexual life. Don’t ignore your body’s signals—take care of yourself today to live better tomorrow.
At the first signs of erectile dysfunction, fill out Dr. Paulo Egydio’s pre-analysis form, a specialist in male health.
A urologist with over 20 years of medical experience, Dr. Paulo Egydio offers personalized care to help patients face challenges related to sexual health.
Learn more:
- Male Self-Care: Why Is It Important for Health?
- Learn All About Enlarged Prostate: Causes, Diagnosis, and Recommended Treatments
- Does Stress Decrease Libido? Learn How to Identify and Treat It
- What Is Ejaculation? Answers to Your Main Questions
- Consequences of Male Sexual Abstinence and the Problems It Can Cause
- 10 Tips for Penis Care to Maintain Health and Prevent Infections and Diseases
- See What Causes Erectile Dysfunction and Available Treatments
- Prostate Surgery: What to Expect, Risks, and Recovery
- Gut Health and Sexual Function: The Connection





