How to increase penis size: surgical and non-surgical methods, always individualized and guided by a urologist.
How to increase penis size is a common curiosity among men, as the organ is tied to ideas of virility and sexual performance. This makes penile enlargement a topic surrounded by unproven approaches and calls for caution.
These procedures should only be considered when medically necessary—such as in cases of micropenis or to address consequences of Peyronie’s disease—and never for purely cosmetic reasons.
The search for options on how to increase penis size must be based on medical guidance and reliable data; otherwise, it may harm male sexual health.
To understand which treatments are effective, who they are indicated for, their risks and, especially, the most common myths about how to increase penis size, keep reading.
Non-surgical methods to increase penis size
Non-surgical options are less invasive and may be used as complementary measures in some cases. However, it is essential to follow a urologist’s recommendations to avoid harm.
Exercises to increase penis size
Penile exercises, such as jelqing, are manual techniques that claim to increase penis size by improving blood circulation and stretching penile tissues. They involve repetitive “milking” movements that could, in theory, increase length and girth.
Efficacy: there is no robust scientific evidence proving these exercises work. Some men report temporary changes, but these are not permanent.
Risks: if performed incorrectly, exercises can injure penile tissue, causing bruising, pain and even erectile dysfunction.
Traction devices
Penile traction devices (extenders) apply a constant stretching force to the penis. The idea is that this tension stimulates cellular growth and, consequently, increased penile length.
Efficacy: a 2023 literature review that analyzed five recent studies found no convincing statistical evidence of size improvement with traction devices, contrary to some older reports.
Risks: improper use can cause discomfort, tissue injury and circulation problems.
See also: How to measure your penis at home
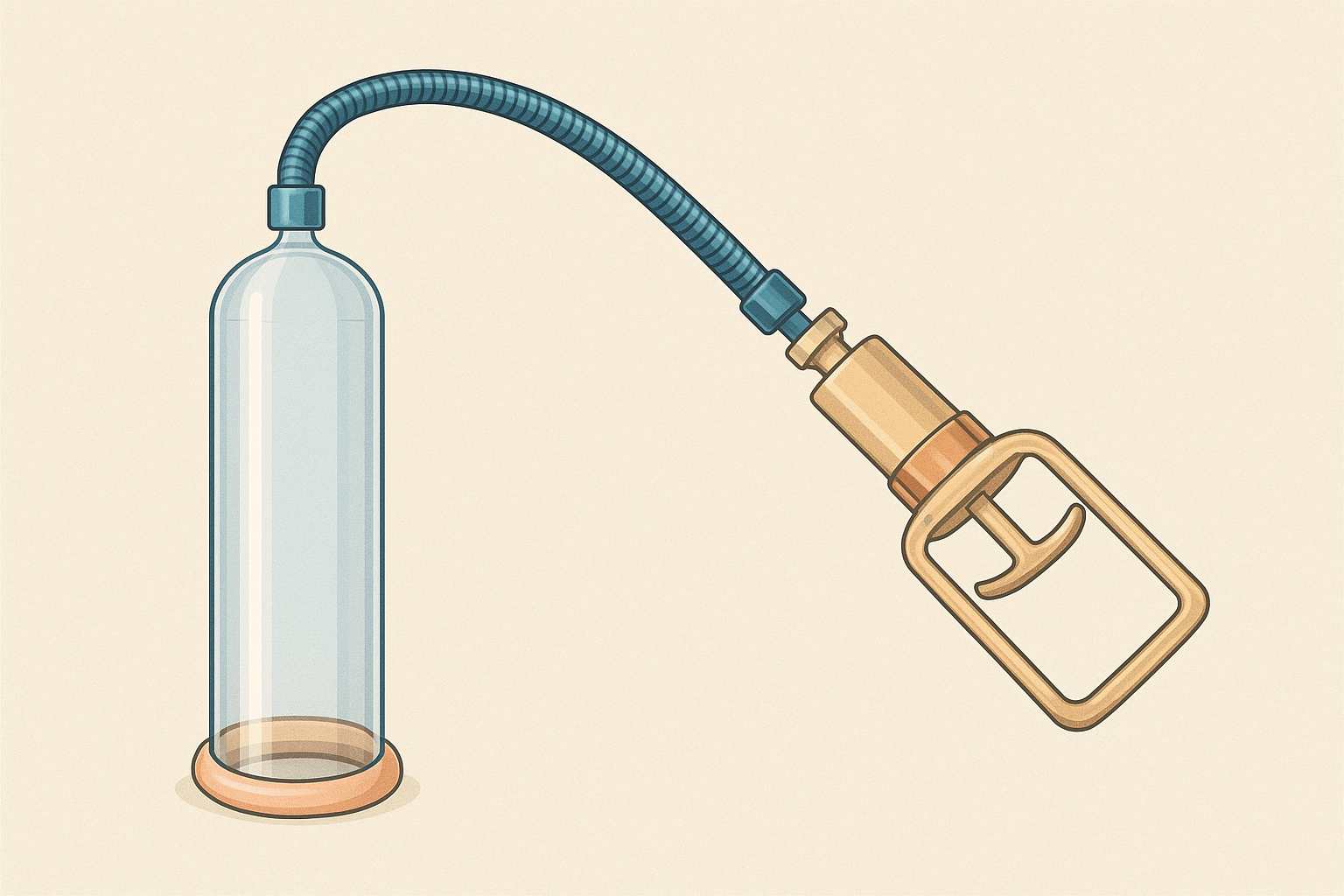
Vacuum pumps
Penis pumps consist of a cylinder, a pump and a constriction ring. The device creates negative pressure around the penis, drawing blood into the corpora cavernosa and producing a temporary erection.
Efficacy: according to a 2023 study in Frontiers in Physiology, vacuum therapy can help treat erectile dysfunction with high success rates and may help preserve penile size; however, the study focused on post-radical prostatectomy penile rehabilitation.
Risks: excessive use may damage blood vessels, leading to bruising and other injuries.
Surgical methods to increase penis size
Cases that do not respond well to exercises or devices may require surgical procedures, as indicated by a urologist.
Suspensory ligament release
This surgery cuts the ligament connecting the penis to the pubic bone. This allows a portion of the internal shaft to project outward, increasing apparent flaccid length.
Efficacy: a 2017 study in Translational Andrology and Urology reported average flaccid gains of 1–3 cm, with no consistent evidence of erect length increase.
Risks: infection, scarring, loss of sensation and erectile dysfunction. Releasing the ligament can also reduce the natural erection angle, compromising rigidity.
Importantly, greater projection does not mean a real increase in total penile size.
Tissue grafting
This technique places tissue grafts to increase girth and size after tissue expansion. Grafts may be autologous, from a donor, or synthetic.
Efficacy: in some cases, dimensions can be modified, but outcomes vary widely depending on the graft type.
Risks: graft rejection, infection, nodules/granulomas, conspicuous scarring, deformities, necrosis, fibrosis, erectile discomfort and potential need for revision surgery.
Penile fillers
Penile filling is a minimally invasive approach using injectable substances such as hyaluronic acid, poly-L-lactic acid or autologous fat to increase girth.
Efficacy: a 2022 multicenter trial in the World Journal of Men’s Health found both hyaluronic acid and poly-L-lactic acid increased girth (~2.3 cm and ~2.0 cm on average, respectively), with no statistically significant difference between them.
Risks: while severe adverse events are uncommon, there can be scarring, asymmetries, deformities, pain and loss of sensitivity. In some cases, partial or total resorption occurs, compromising aesthetic and functional expectations.
Phalloplasty
Phalloplasty aims to increase penile length or girth for aesthetic modification, whether due to gender-affirming needs, medical conditions or other reasons.
Results vary and should be discussed realistically between patient and specialist, considering risks and limitations.
This approach does not apply to treating Peyronie’s disease or other specific medical conditions.
Efficacy: may improve appearance and, in some patients, body image and confidence, depending on clinical context and individual response.
Risks: infection, visible scarring, sensory and circulatory changes, and urethral narrowing or obstruction.
Egydio’s Technique
The Egydio Technique is an adjunct maneuver—a complementary surgical step—used during correction of Peyronie’s disease. Its goal is to increase surgical precision, enabling not only penile straightening but also expansion of length and girth during deformity repair.
The surgery applies geometric principles to the tunica albuginea, allowing curvature correction and restoration of proportionality when treating erectile dysfunction.
Unlike purely aesthetic procedures, Egydio’s Technique aims to preserve erectile function and organ symmetry whenever possible. Not every patient has an indication for Peyronie’s surgery with this technique.
Efficacy: may provide penile alignment, improved penetrative capacity and functional gains; anatomical changes vary by severity and individual response.
Risks: pain, bruising, infection and poor wound healing. If not performed with penile prosthesis placement, it does not directly treat erectile dysfunction.
The importance of consulting a urologist
Any plan on how to increase penis size should be approached with caution and reliable information. Before making decisions, consult a urologist.
There is no pill to increase penis size. A physician must assess each case, determine whether there is a clinical indication, recommend the most appropriate approach, and explain the risks and benefits.
Penile enlargement procedures require a clear clinical indication. They are generally considered for men who have lost dimensions over time due to conditions such as Peyronie’s disease.
In such cases, reconstructive techniques—such as the Egydio Technique—may help restore anatomy and improve functionality, always aiming to preserve sexual health and minimize risks.
Interest in enlargement is often linked to male self-esteem and cultural associations with virility. Even so, it’s essential to avoid experimental or unproven methods that may pose unnecessary risks.
Book an appointment with Dr. Paulo Egydio
Before considering any method to increase penis size, speak with urologist and andrologist Dr. Paulo Egydio.
Many methods promise quick, easy—and costly—results, but few have robust scientific evidence supporting their efficacy and safety.
With over 25 years in the field and international academic experience, Dr. Paulo Egydio guides patients based on evidence and individualized evaluation.
Fill out the pre-analysis form and allow up to 24 hours to start receiving guidance. The consultation is the first step to determine whether there is a clinical indication and which options may be discussed safely.
Learn more:
-
- Most common prostate diseases and symptoms
- Penis types: differences, myths and facts
- Male Masturbation: Benefits and Myths
- Male hormones that influence your health
- 10 Tips to Improve Sexual Performance
- What Is Ejaculation? Your Top Questions Answered
- What Is Andropause? Signs, Symptoms and Treatments
- The 4 Main Penile Surgeries: Are They Effective?
- Penis Anatomy: Structure, Erection and Ejaculation
- Top 10 penile diseases: what they are and how to treat
- Penile pain: 12 causes, symptoms and treatments