Andropause (“male menopause”) is a natural aging process characterized by the gradual reduction of testosterone levels.
The term andropause, also called late-onset male hypogonadism, describes the hormonal changes that occur with advancing age. This condition is associated with a progressive decrease in testosterone, the main male sex hormone.
Below, learn how to identify early signs of andropause and the medical approaches used to manage symptoms and support quality of life during this phase.
What is andropause?
Andropause refers to a set of symptoms and hormonal changes.
At what age does andropause start in men?
This hormonal change affects men as they age, especially from age 40 onward.
Unlike menopause in women, andropause does not involve an abrupt end to the production of male sex hormones; it is a gradual and natural decline in testosterone levels.
Testosterone is the main male sex hormone, responsible for regulating several functions in the body, such as the development of sexual organs, sperm production, muscle mass, bone density, fat distribution, and libido.
As men get older, they experience a mild and gradual decline in testosterone levels, usually starting around age 30, which may intensify with andropause.
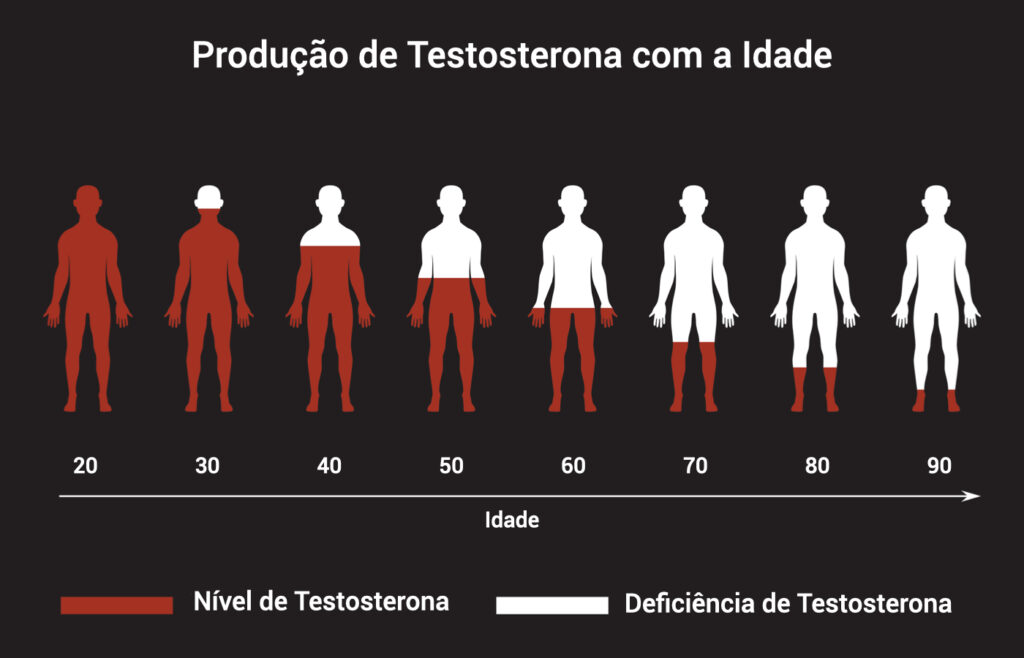
Chart with male silhouettes representing testosterone production from ages 20 to 90.
What are the symptoms of andropause?
Early signs of andropause can appear gradually, affecting different aspects of men’s health.
These symptoms may go unnoticed at first, but paying attention helps identify andropause early.
Common andropause symptoms include:
- Reduced libido and sexual interest
- Low energy and fatigue
- Mood changes, such as irritability and anxiety
- Difficulty concentrating
How do I know if I’m going through andropause?
Andropause usually starts from age 40, but it may appear earlier or later depending on the individual.
What does a man feel during andropause?
Gradual reduction in libido, persistent fatigue, and mood changes (such as mild irritability) are common early signs.
These symptoms can begin subtly and intensify, affecting emotional and physical well-being.
Regardless of symptom intensity, it is advisable to consult a specialist physician to confirm the diagnosis.
Regular appointments with a urologist are important, as they can order tests to identify andropause and other hormonal issues early.
How is andropause diagnosed?
The diagnosis is based on a combination of clinical symptoms and specific laboratory tests. The main steps include:
Symptom assessment
The physician conducts a detailed interview to understand the patient’s reported symptoms.
This includes symptoms such as decreased libido, fatigue, mood changes, reduced muscle mass, and sexual difficulties.
Physical examination
A physical exam may be performed to check for signs associated with andropause, such as increased abdominal fat and loss of muscle mass.
Laboratory tests
The main test for diagnosing andropause is measuring total serum testosterone.
Blood is usually drawn in the morning, when testosterone levels are highest.
If levels are below normal for the patient’s age, andropause may be considered.
If tests confirm the condition, the physician may evaluate the indication for testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).
Excluding other conditions
It is important to rule out other medical conditions that may cause similar symptoms, such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, or depression.
Assessing symptom impact
In addition to physical and laboratory exams, the physician assesses the impact of symptoms on quality of life. Questionnaires may be used to evaluate sexual function, mood, and energy.
Medical follow-up
Based on test results and symptom assessment, the physician can make the diagnosis of andropause and discuss treatment options if needed.
Does andropause have a cure?
Andropause does not have a “definitive cure,” in the sense of reversing the natural process of male hormonal aging.
However, there are effective treatment options to manage symptoms and support quality of life in affected men.

Man wearing a green long-sleeve shirt and brown pants talking to a doctor with a clipboard; an ultrasound-like device is nearby.
What treatments are available for andropause?
Each case is unique, and the ideal plan should be personalized based on symptoms, overall health, and patient preferences. Main options include:
Hormone replacement
The physician may prescribe male hormone replacement after tests indicate testosterone levels.
How is andropause treated? Options include topical, transdermal, and injectable TRT.
- Topical: testosterone gels applied once daily to shoulders, arms, or abdomen; the skin absorbs and releases hormone gradually.
- Transdermal: daily testosterone patches (often on the abdomen). Another transdermal option is a subcutaneous testosterone implant, placed in an outpatient procedure.
- Injectable: testosterone injections may be weekly, biweekly, or every two to three months, depending on the formula.
Is testosterone replacement therapy safe?
TRT may be considered safe when indicated and monitored by a specialist, but requires individualized evaluation of risks and benefits.
This article on the effects of testosterone replacement analyzed research conducted between 1990 and 2023 with 3,461 patients.
According to the study, TRT was associated with improved erectile function in some patients with hypogonadism.
This response was reported particularly in studies with testosterone gel use for more than 30 weeks.
However, even with scientific evidence of potential benefits, individual responses vary.
What are the risks and benefits of hormone therapy?
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) has potential benefits and risks.
Key points include:
- Symptom relief
- Quality-of-life support
- Maintenance of muscle and bone mass
- Potential cardiovascular effects (benefits and risks)
- Increased risk of blood clots
- Prostate cancer considerations
- Side effects
- Impact on fertility
Healthy lifestyle
Reduced testosterone—a feature of andropause—can affect physical drive and motivation.
Regular exercise and a balanced diet rich in vitamins, fiber, and proteins are essential.
Dark chocolate, strawberries, and salmon, for example, may support blood flow—important for erectile function.

Visit the YouTube channel for more men’s health content
Beyond the blog, Dr. Paulo’s YouTube channel offers many tips on men’s health. Subscribe and enjoy!
Book your consultation with Dr. Paulo Egydio
Andropause can impact men’s health, and specialized care may help manage symptoms and support quality of life.
If you suspect you’re going through this phase, fill out the pre-analysis form to receive initial guidance by email.
Learn more:
- Men’s sexual health: 7 habits that affect performance and how to improve
- Check-up exams for men over 50
- Sex After 60: How to Stay Active?
- Sex After 50: 11 Tips to Keep the Spark Alive
- Until what age does a man ejaculate?
- Up to what age can a man have sex?
- Pelvic Floor Strengthening: Why and How
- Andrologist: Everything About This Specialist





